With the help of various machine learning techniques, the researchers hope to gain a better understanding of how real estate pricing performs. In the aim, a methodology developed that categorizes pricing performance based on certain provinces in general rather than specific provinces in particular. In this study, multi layer perception, naive-Bayes, and random forest algorithms used to solve the problem.
The data used in this study came from the real estate market. Nine classes, two columns, and seventeen hundred and thirteen rows make up the training data set. In addition, they have been developed using the WEKA software package.
Results classified into three categories based on how they measured. A training set, five-fold cross-validation, and ten-fold cross-validation are all used in this study. The training set used as the test data set, and the test data set is used as the training data set again. Cross-validation is a technique in which a portion of the training data set is used as the test data set.
Multi-Layer Perceptrons
Parameters: • hiddenLayers: 3 • learningRate: 0.5 • momentum: 0.2 • trainingTime (iteration count): 1000
Use Training Set
According to classification success, TP Rate accuracy is 82% and ROC Area accuracy is 95%. The confusion matrix shown below.

5 Fold Cross-Validation
According to classification success, TP Rate accuracy is 55% and ROC Area accuracy is 83%. The confusion matrix shown below.

10 Fold Cross-Validation
According to classification success, TP Rate accuracy is 53% and ROC Area accuracy is 82%. The confusion matrix shown below.
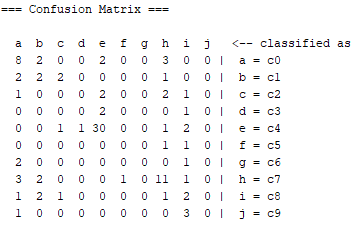
Naive Bayes
Use Training Set
According to classification success, TP Rate accuracy is 81% and ROC Area accuracy is 96%. The confusion matrix shown below.
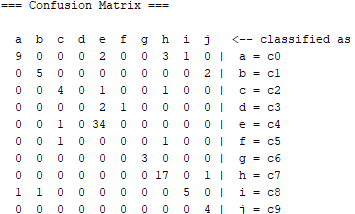
5 Fold Cross-Validation
According to classification success, TP Rate accuracy is 65% and ROC Area accuracy is 89%. The confusion matrix shown below.
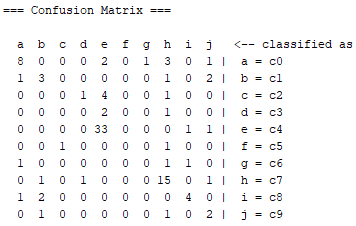
10 Fold Cross-Validation
According to classification success, TP Rate accuracy is 64% and ROC Area accuracy is 89%. The confusion matrix shown below.
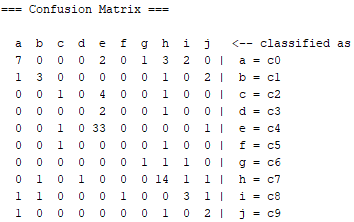
Random Forest
Use Training Set
According to classification success, TP Rate accuracy is 100% and ROC Area accuracy is 100%. The confusion matrix shown below.

5 Fold Cross-Validation
According to classification success, TP Rate accuracy is 65% and ROC Area accuracy is 89%. The confusion matrix shown below.

10 Fold Cross-Validation
According to classification success, TP Rate accuracy is 64% and ROC Area accuracy is 89%. The confusion matrix shown below.
When comparing MLP accuracy, the use of a training set yielded the most accurate results in the study. The cross-validation with a tenfold increase in accuracy had the lowest accuracy. The maximum accuracy measured in the ROC Area was 95%, which considered to be excellent. The accuracy in TP Rate measured at 53 percent, which was the lowest in the group. The parameters are always the same.
When comparing accuracy for naive bayes, the use of a training set resulted in the highest level of precision. The cross-validation with a tenfold increase in accuracy had the lowest accuracy. In the ROC Area, the maximum accuracy measured to be 96 percent, which considered excellent. Sixty-four percent determined to be the lowest accuracy in TP Rate.
Comparing the accuracy of random forests, the use of a training set yielded the most accurate results. The cross-validation with a tenfold increase in accuracy had the lowest accuracy. In both the ROC Area and the TP Rate, the highest accuracy determined to be 100 percent. Sixty-four percent determined to be the lowest accuracy in TP Rate.
Among all of the algorithms tested, the random forest was found to have the highest accuracy in both the ROC Area and the TP Rate. In terms of TP Rate accuracy, MLP was the least accurate.
If you are curious about multi layer perceptions, you can get more info with this article.
Please click for more information.
















Add Comment